CESR Applications for Psychiatrists
- April 25, 2022

In this article, we’ll be taking a closer look at the specific guidance on NHS applications for entry onto the Specialist Register through the Certificate of Eligibility for Specialist Registration (CESR) for psychiatrists.
We’ll cover the eligibility criteria, application process, and most importantly the required evidence, along with some other topics, summarised in the headings below:
- What is CESR and who is it for?
- Do overseas psychiatrists need MRCPsych for CESR?
- What is the CESR equivalence process?
- What evidence is required for a CESR in psychiatry?
- Where will I find this evidence?
- Submitting a CESR Application
- How much does CESR cost?
- How long does it take to receive a decision?
- How long does it take to complete?
- Do I have to complete CESR before I can work in the UK?
- #IMG Tips
- How do I get started?
Skip ahead to the relevant section if you know what you’re looking for.
An Introduction to CESR
The CESR, or Certificate of Eligibility for Specialist Registration, is the route to specialist registration for psychiatrists who have not completed a GMC-approved training programme but who are able to demonstrate that their specialist training, qualifications and experience are equivalent to the requirements for the award of CCT in the UK.
CESR holders can be appointed to substantive (or permanent) consultant positions in the NHS. As a psychiatrist, attaining specialist registration will mean you are qualified to practice independently as a psychiatry consultant in the NHS.
Psychiatrists must satisfy the GMC that their specialist training or specialist qualifications, when considered together, are equivalent to a CCT in the specialty in question. Doctors who have undertaken a minimum of 6 months training or obtained a specialist qualification and acquired specialist medical experience or knowledge as a psychiatrist within a non-training post, and are currently practicing, may apply to the GMC for assessment of their competencies.
Overseas doctors do not require CESR before moving to the UK to work in the NHS. Often, experienced psychiatrists will secure a post in the UK, and work towards CESR whilst in post. Typically, CESR is a preferred route towards specialist registration for overseas trained psychiatrists.
An overseas psychiatrists training may not have covered all the ground of the CCT curriculum, but they may be able to show competence in the missing area through experience in a fixed term Specialty Doctor, Specialty Grade, Associate Specialist, or Acting Consultant post in the NHS. In this case, overseas psychiatrists will likely complete the MRCPsych exams to gain GMC registration and start working in the NHS, before completing CESR.
MRCPsych for Specialist Registration
Overseas doctors looking to join the Specialist Register are not required to have completed the Royal College postgraduate exams. In this case, MRCPsych is only a requirement for doctors looking to attain Specialist Registration via the CCT route.
The standard test of knowledge in the CCT curriculum is the MRCPsych exam, so passing these exams confirms the attainment of the competencies of the core Curriculum.
However, if CESR applicants have not successfully completed MRCPsych, they must provide alternative evidence that demonstrates equivalent knowledge to psychiatrists who have passed the exams.
Even if the competencies covered by the exam require something that someone in your position would not routinely undertake (in your sub-specialty for example), you must still provide evidence of it – as the evaluators will not make assumptions outside of the evidence presented.
This is not to be confused with the requirements for registering for a full licence to practice with the GMC – many overseas applicants choose to complete MRCPsych.
Specialist Registration is additional to full registration with the GMC and is therefore not required to practice as a psychiatrist in the UK.
You can read more about the full MRCPsych examination suite in our IMG Resources library.
The CESR Equivalence Process
Equivalence refers to the process of assessing an overseas applicant’s training and experience against the current psychiatry training programme requirements, in order to be awarded CESR.
The equivalence process involves submitting a written body of evidence to the GMC, consisting of:
- training and/or competence; AND
- skills and knowledge
The Royal College of Psychiatrists will assess each application against the relevant Curriculum before providing a recommendation to the GMC, who will then make a decision.
Please note that Equivalence procedures are the responsibility of the GMC. Applications are made through their Certification Department and initial enquiries should be directed there.
Evidence Requirements for CESR in Psychiatry
Skills & Experience: The evidence provided for a CESR application in psychiatry must cover the knowledge, skills and qualifications to demonstrate the required competencies in all areas of the General Psychiatry Curriculum, and the Advanced Module in the sub-specialty you are applying in. If evidence is missing from any area of the curriculum, the application will fail.
Primary Evidence: To demonstrate that you can do what is required by the curriculum, you need to submit primary evidence of your clinical practice which shows how you work on a day-to-day basis: letters, reports, assessments etc. References, retrospective case summaries, and reflective notes can all be used in a CESR application, but by themselves they are not sufficient.
Audit & Governance: You are required to submit evidence of your active leadership in audit, including evidence that you have completed at least one audit cycle
Currency of evidence: Your evaluators will be looking for evidence of current competency, generally defined as within the last five years. If you have completed training before this point, it is crucial that you provide evidence of maintaining competency across the whole area of the curriculum.
The GMC asks that only evidence that is strictly relevant is sent as it will help them to process the application quicker. The guidance on compiling your evidence will help you to decide what is relevant and what is not – you can find this on the GMC website here.
As a general guide, the GMC usually expects to see about 800 - 1200 pages of evidence, divided into four different domains, reflecting those of Good Medical Practice. The GMC recommends that you apportion the evidence provided as shown below:
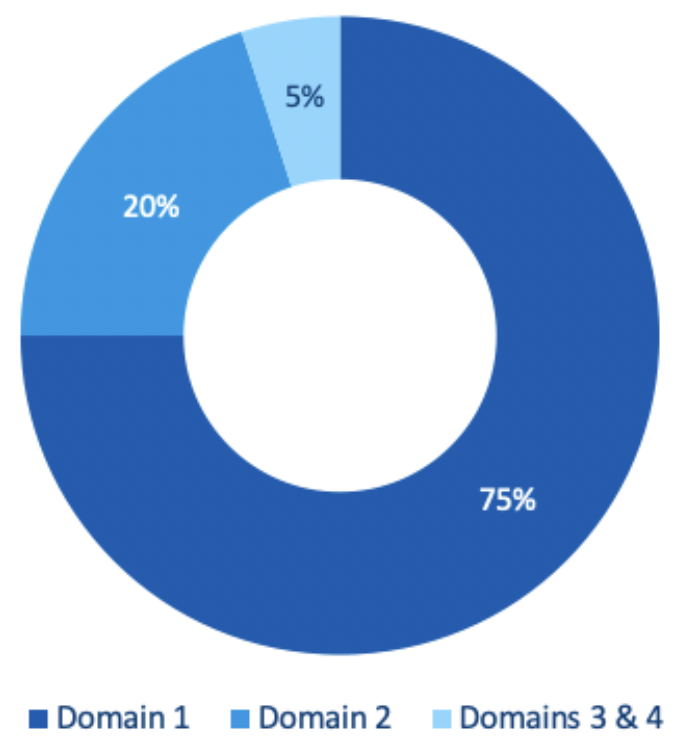
Domain 1 – Knowledge, skills and performance
Domain 2 – Safety and quality
Domain 3 – Communication, partnership and teamwork
Please note, you cannot compensate for evidence lacking in one area by providing more evidence in another area.
The full list of evidence required for each domain can be found on the GMC website here.
Gathering Evidence for a CESR Application
Domain 1 – Knowledge, skills and performance
Qualifications
- Primary Medical Qualification (PMQ)
- Specialist medical qualification(s)
- Curriculum or syllabus (if undertaken outside the UK)
- Specialist registration outside the UK
- Honours and prizes
- Other relevant qualifications
Assessments and appraisals
- Appraisals and assessments
- RITAs, ARCPs and training assessments
- 360˚ and multi-source feedback
- Awards and discretionary points letters
- Personal development plans (PDP)
Logbooks, records of daily clinical practice and portfolios
- Logbooks
- Consolidation, cumulative data sheets, summary lists and annual caseload statistics
- Medical reports
- Case histories
- Referral letters discussing patient handling
- Patient lists
- Departmental (or trust) workload statistics and annual caseload statistics
- Rotas, timetables and job plans
- Portfolios (electronic or revalidation)
Details of posts and duties (including both training and experience posts)
- Employment letters and contracts of employment
- Job descriptions
- Job plans
Research, publications and presentations
- Research papers, grants, patent designs
- Publications within specialty field
- Presentations, poster presentations
CPD and CME
- CPD record certificates, certificates of attendance, workshops and at local, national and international meetings or conferences
- CPD registration points from UK Medical Royal College (or equivalent body overseas)
- Membership of professional bodies and organisations
- Teaching timetables
- Lectures
- Feedback or evaluation forms from those taught
- Letters from colleagues
- Attendance at teaching or appraisal courses
- Participation in assessment or appraisal and appointments processes
Domain 2 – Safety and quality
Participation in audit, service improvement
- Audits undertaken by applicant
- Reflective diaries
- Service Improvement and clinical governance meetings
Safety
- Health and safety
Domain 3 - Communication, partnership and teamwork
Communication
- Colleagues
- Patients
Partnership and teamwork
- Working in multidisciplinary teams
- Management and leadership experience
- Chairing meetings and leading projects
Domain 4 – Maintaining trust
Acting with honesty and integrity
- Honest and integrity
- Equality and human rights (including disability, human rights, race, religion and ethnicity awareness and equal opportunities)
- Data protection
Relationships with patients
- Testimonials and letters from colleagues
- Thank you letters, cards from colleagues and patients
- Complaints and responses to complaints
Additional areas of evidence
Topics Covered in the MRCPsych Exams
Paper A:
- Behavioural science and sociocultural psychiatry
- Basic psychology
- Social psychology
- Social science and sociocultural psychiatry
- Human development
- Basic neurosciences
- Neuroanatomy
- Neurophysiology
- Neurochemistry
- Molecular genetics
- Neuropathology
- Clinical psychopharmacology
- General principles
- Pharmacokinetics
- Pharmacodynamics
- Adverse drug reactions
- Classification and assessment in psychiatry
Paper B:
Organisation and delivery of psychiatric services
General adult psychiatry
- Prevalence/incidence, aetiology, presentation, treatment and outcome of psychiatric disorder in adulthood
- Disorders related to pregnancy and childbirth
- General hospital psychiatry
- Emergency psychiatry
- Eating disorders
- Psychosexual disorders
Old age psychiatry
Psychotherapy
- Dynamic psychotherapy
- Family therapy
- Cognitive-behavioural therapies
- Other therapeutic models
- Effectiveness of psychotherapy
- Group therapy
Child and adolescent psychiatry
Substance misuse/addictions
Forensic psychiatry
- Relationship between crime and mental disorder
- Psychiatry and the criminal justice system
- Practicing psychiatry in a secure setting
- Human rights legislation as it affects patients and psychiatric practice
Learning disability
- Services
- Epidemiology/Aetiology
- Clinical
Research methods, statistics, critical review and evidence-based practice
- Translation of clinical uncertainty into an answerable question
- Systematic retrieval of the best available evidence
- Critical appraisal of the evidence
- Application of the results in practice
Evaluation of performance
All these topics covered in the MRCPsych exams can be found in the Core Training in Psychiatry curriculum.
For more guidance on the different types of evidence, see the specialty specific guidance from the GMC for psychiatry.
Validating the evidence
Original documents which are on headed paper with a hospital stamp and original signatures do not need additional validation.
All photocopied evidence should contain a hospital stamp on every page of each document, the validator’s name (printed and in full), job title (printed and in full) and original signature.
Submitting a CESR Application
All CESR applications are submitted online via GMC Online and if you have not already created an account, you can find a guide on how to do so here.
Electronic evidence is required for each of the different evidence sections of the CESR application. Once started, the online application remains open for 12 months, meaning that it can be used as a portfolio to gather evidence against each of the different sections.
Your electronic evidence can be in any of the following formats:
- .doc
- .ppt
- .xls
Formats outside of these are unlikely to be accepted.
The Online Application
You will be required to complete the following sections once you begin your application:
- Specialty details
- Qualification details and professional experience
- Details of your referees
- Registration and licensing history
- Evidence summary
- Details of your verifiers
- Final declaration and payment
Additional Evidence
Once an Adviser on the Specialist Applications Team has reviewed your initial evidence, they will provide you with information on:
- What evidence they’ve accepted
- What evidence they’re unable to accept (including the reasons for this)
- Advice and guidance on how your application could be strengthened
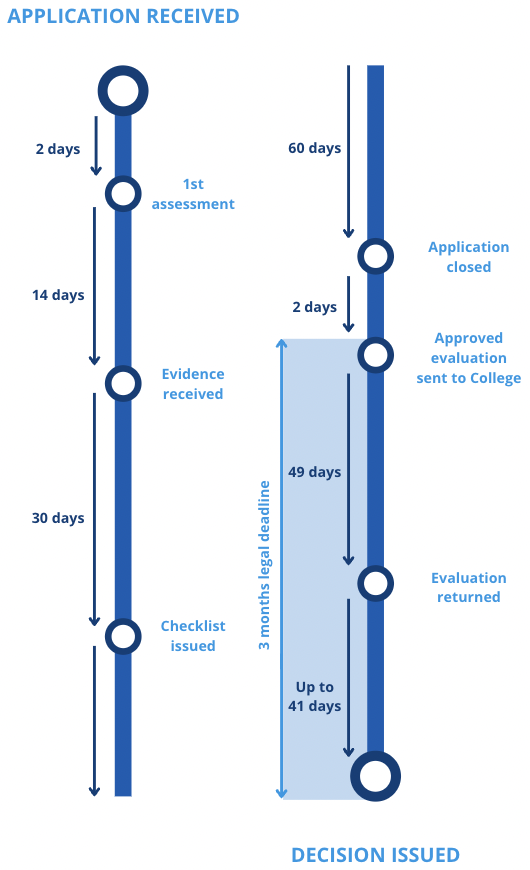
You’ll have up to 60 days to provide additional documentary evidence in support of your application (30 days if you’ve submitted a Review application).
For further information about the online application process, see the GMC’s User Guide.
The Cost of CESR Applications
All psychiatrists applying for Specialist Registration must pay a fee. For CESR, this fee is £1,676. For CESR-CP and CCT, the cost is £439.
How long does it take to receive a decision?
The GMC estimate that it can take between six and eight months to receive a decision, from the date you submit your CESR application.
How long does it take to complete?
As there is a substantial amount of evidence to gather for a CESR application, the process of preparing all the necessary documentation and applying for CESR can take even longer than this, and a typical candidate will usually set out to complete this within 1 – 3 years.
It is worth noting that more senior psychiatrists, such as consultants, are more likely to have achieved all the competences outlined in the curriculum.
The indicative period of training for a CCT in psychiatry is six years, so it is highly unlikely that you would achieve the competencies required for a CCT in a shorter period of time. Therefore, CESR is not suitable for more junior psychiatrists.
NHS Positions in the NHS without CESR
It is important to note that you can apply for more senior psychiatry roles such as a specialty doctor (SAS), specialist grade or acting consultant without being on the Specialist Register.
Similarly, overseas doctors do not require CESR before moving to the UK to work in the NHS.
When compared to a trainee post, you will likely receive better pay and responsibilities that are more appropriate to your level of experience. While working in these positions, you can collect evidence of your competences, particularly those specific to the UK psychiatry curriculum.
Across the UK there are several NHS Trusts with well-established CESR programmes of support for psychiatrists who have taken up a fixed term post with the view to completing CESR.
These positions also facilitate a faster route to working in UK and attaining Specialist Registration when compared to making an application for CESR from overseas, which can take an additional amount of time.
#IMG Tips
- Research/think about the types of evidence you will need and begin to gather your evidence well in advance of making your application.
- Gather evidence prospectively – this is much easier than retrospectively trying to pull together the evidence under additional pressures.
- Make sure that your evidence is of the highest possible quality and is current – you will be assessed against the most recent curriculum.
- Ensure that the evidence you collect demonstrates your competence across the whole of the psychiatry curriculum, not just your sub-specialty.
- Remember to refer to the most up-to-date Psychiatry CCT Curriculum and Specialty Specific Guidance for the evidence requirements in your specialty.
- Create a CESR ‘to-do list’ with sections under the GMC’s 4 domain headings – organise your evidence directly into these sections to manage your progress.
- Do not submit original documents – all your copies, other than qualifications you’re getting authenticated must be accompanied by a proformas signed by the person who is attesting to the validity and accuracy of your evidence (your verifier).
- Choose your referees carefully - they will need to be able to comment on direct observation of your clinical competences. At least six (from the last 5 years) are required but it would be preferable to give provide eight to ten (based on previous experience).
- Reconstruct your CV from scratch so that it matches the application form - if you submit a CV that doesn’t contain the required information or you have not submitted all evidence as mentioned on the CV, this will delay your application.
- Request a CV consultation with one of our experts
- Ask an IMG Connect recruitment specialist about NHS psychiatry posts with CESR support. These are not always advertised by a Trust, but we can help you find a role which aligns well with your career goals in the NHS.
- Join the IMG Psychiatrists community – as well as support on Royal College exams, our online community of international psychiatrists and dedicated psychiatry recruiters offers guidance on other aspects of working in the UK, including finding NHS posts and CESR.
Getting started
Attaining Specialist Registration through the CESR pathway can be a long but very rewarding process. Look at our introduction to CESR for psychiatrists for a full overview.
If you have any further questions about Specialist Registration, your route to the UK, or would like guidance in finding NHS posts which offer CESR support, please get in touch with us here.
To receive the latest news and updates on all things psychiatry, including the Royal College, GMC registration and the NHS, follow us on social media and join the conversation.
Relevant Jobs
A leading NHS mental health hospital in the East of England is looking for a Consultant Psychiatrist in Old Age Psychiatry with a focus on functional illness within inpatient care. The service sits within a well-integrated healthcare system combining mental and physical health services. The post is based on a 22-bed ward, supported by a multidisciplinary team including psychologists, occupational therapists, physiotherapists, and speech and language therapists. This Old Age Psychiatry job is open to both international and UK-based doctors, with MRCPsych or EEA specialist certification most encouraged to apply.
Anyone requiring portfolio support (formally known as CESR) can have their required support discussed on a case-by-case basis.
JOB REQUIREMENTS AND DETAILS-
Consultant level experience in old age psychiatry
-
Be eligible for GMC registration, either with MRCPsych (Full), or EEA specialist certification
-
Consultants with an interest and prior experience in old age psychiatry and inpatient functional illness should apply
-
The salary will be between £105,504 to £139,882 dependent on experience or grade
-
Provide medical oversight and psychiatric input for 22 beds (14 for functional illness, 8 for organic illness) on an inpatient ward
-
Conduct psychiatric assessments, care planning, and contribute to regular MDT reviews
-
Supervise junior doctors and support their training and development
-
Collaborate with community teams including the Crisis Resolution and Home Treatment Team for Older People (CRHTT-OP)
-
Liaise with other services such as social care, physical health teams, and voluntary sector partners to ensure coordinated care
-
Engage in clinical documentation, audits, research, and educational activities
LIFE IN THE REGION
This region offers a balance of vibrant urban living and tranquil countryside settings. From lively city centres with extensive amenities to quiet villages rich in charm, there’s something for everyone. The area benefits from excellent rail and road connections (50 minutes to London) high-performing schools, and a diverse mix of leisure and cultural attractions.
Steeped in history, the region is known for its architectural heritage and community spirit, making it a highly desirable location for professionals and families alike.
HOW WILL IMG CONNECT SUPPORT YOU?When applying with IMG Connect you’ll have the full support of an expert recruitment team who will be your recruitment and relocation partners throughout the process. We\'ll support you with:
-
CV Preparation with a bespoke session with one of our specialists
-
Application support with expert knowledge of NHS specialisms & recruitment practice
-
At least two video calling interview preparation sessions
-
Contract and offer negotiations for salary, relocation packages, tenure, and more
Once you have accepted your new role, you’ll then be supported and led throughout by one of our dedicated relocation executives who will guide you all the way to starting your new post, including:
-
Document gathering and checking
-
COS and Visa Application support if applicable
-
Support sourcing short- and long-term accommodation
-
Travel arrangements
-
Family support for finding schools and any other aspects of pastoral care
An NHS Board in Eastern Scotland is looking for a Consultant Psychiatrist with experience in Old Age Psychiatry to lead an outpatient community team.. The Psychiatry department comprises a team of psychiatrists and multidisciplinary professionals including Nurse Team Lead, Community Mental Health Nurses, Community Mental Health Nurses, Healthcare Support Workers, Care Home Liaison Nurses, Young Onset Dementia Nurse, Occupational Therapists, Psychologist, Dementia Post Diagnostic Support, Care managers, DPDS Link Worker, Alzheimer Scotland Link Worker.
This Psychiatry job is open to both international applications and UK-based doctors, though those with European Specialist or MRCPsych or equivalent are most encouraged to apply.
Anyone requiring portfolio support (formally known as CESR) can have their required support discussed on a case-by-case basis.
JOB REQUIREMENTS AND DETAILS
-
Consultant level experience in psychiatry
-
Be eligible for GMC registration, either with MRCPsych (Full), or EEA specialist certification
-
Prior experience in Old Age mental health care.
Anyone with consultant experience in old age psychiatry should apply. The salary will be between £107,144 - £142,369 per annum, dependent on experience or grade.
CORE DUTIES OF THIS ROLE
-
Provide clinical leadership and management in Old Age Psychiatry services.
-
Supervise junior doctors and contribute to their training and professional development.
-
Work closely with multidisciplinary teams to deliver high-quality patient care.
-
Participate in service development and improvement initiatives within the department.
LIFE IN SCOTLAND
This location offers a blend of urban convenience and rural tranquillity, with easy access to major cities such as Edinburgh, Dundee, and Glasgow. Whether you prefer city living with vibrant culture and nightlife or coastal and countryside retreats with stunning landscapes, there are plenty of options.
The region has excellent transport links, making commuting easy, and offers high-quality schools and a wealth of recreational activities, including outdoor pursuits, cultural festivals, and family-friendly attractions.
Scotland is steeped in history, known for its ancient castles, famous universities, and contributions to global innovation. The country provides a unique cultural experience, rich in traditions and scenic beauty.
HOW WILL IMG CONNECT SUPPORT YOU?
When applying with IMG Connect you’ll have the full support of an expert recruitment team who will be your recruitment and relocation partners throughout the process. We\'ll support you with:
-
CV Preparation with a bespoke session with one of our specialists
-
Application support with expert knowledge of NHS specialisms & recruitment practice
-
At least two video calling interview preparation sessions
-
Contract and offer negotiations for salary, relocation packages, tenure and more
Once you have accepted your new role, you’ll then be supported and led throughout by one of our dedicated relocation executives who will guide you through all the way to starting your new role including:
-
Document gathering and checking
-
COS and Visa Application support if applicable
-
Support sourcing short- and long-term accommodation
-
Travel arrangements
-
Family support for finding schools and any other aspects of pastoral care
Anyone requiring portfolio support (formally known as CESR) can have their required support discussed on a case-by-case basis.
JOB REQUIREMENTS AND DETAILS
- Consultant level experience in psychiatry
- Be eligible for GMC registration, either with MRCPsych (Full), or EEA specialist certification
- Prior experience in adult community mental health care is desirable.
Anyone with an interest in community or inpatient psychiatry should apply. The salary will be between £107,144 - £142,369 per annum, dependent on experience or grade.
CORE DUTIES OF THIS ROLE
- Provide clinical leadership and management in General Adult Psychiatry services.
- Supervise junior doctors and contribute to their training and professional development.
- Work closely with multidisciplinary teams to deliver high-quality patient care.
- Participate in service development and improvement initiatives within the department.
LIFE IN SCOTLAND
This location offers a blend of urban convenience and rural tranquillity, with easy access to major cities such as Edinburgh, Dundee, and Glasgow. Whether you prefer city living with vibrant culture and nightlife or coastal and countryside retreats with stunning landscapes, there are plenty of options.The region has excellent transport links, making commuting easy, and offers high-quality schools and a wealth of recreational activities, including outdoor pursuits, cultural festivals, and family-friendly attractions.
Scotland is steeped in history, known for its ancient castles, famous universities, and contributions to global innovation. The country provides a unique cultural experience, rich in traditions and scenic beauty.
HOW WILL IMG CONNECT SUPPORT YOU?
When applying with IMG Connect you’ll have the full support of an expert recruitment team who will be your recruitment and relocation partners throughout the process. We\'ll support you with:
- CV Preparation with a bespoke session with one of our specialists
- Application support with expert knowledge of NHS specialisms & recruitment practice
- At least two video calling interview preparation sessions
- Contract and offer negotiations for salary, relocation packages, tenure and more
Once you have accepted your new role, you’ll then be supported and led throughout by one of our dedicated relocation executives who will guide you through all the way to starting your new role including:
- Document gathering and checking
- COS and Visa Application support if applicable
- Support sourcing short- and long-term accommodation
- Travel arrangements
- Family support for finding schools and any other aspects of pastoral care
An NHS mental health hospital in the North West of England is looking for a Consultant in Old Age Psychiatry, with an interest in both functional and organic disorders. The Mental Health department is part of a well-established multidisciplinary team, working alongside Consultants, Specialty Doctors, and various healthcare professionals. This psychiatry job is open to both international applicants and UK-based doctors, though those with MRCPsych (Full) or an EEA equivalent qualification are most encouraged to apply.
Anyone requiring portfolio support (formally known as CESR) can have their required support discussed on a case-by-case basis.
JOB REQUIREMENTS AND DETAILS
- Minimum of two years\' experience in old age psychiatry.
- UK applicants with CTT and S12 and AC status preferred
- Be eligible for GMC registration, either with MRCPsych (Full) or an EEA qualification.
- Prior experience in old age inpatient mental health care is desirable.
- The salary will be between £105,504 - £139,882 per annum, dependent on experience or grade.
CORE DUTIES OF THIS ROLE
- Provide psychiatric care and assessments for adult and older adult patients with both functional and organic mental health conditions.
- Work closely with other Consultants, specialty doctors and the multi-disciplinary team to support care planning and patient management.
- Run inpatient services and contribute to continuity of care between community and inpatient settings.
LIFE IN THIS UK REGION
This region offers a mix of urban and rural living, with bustling towns and peaceful countryside options for residents. The area boasts excellent transport links, making it easily accessible from major UK cities. There are highly rated schools, a variety of leisure facilities, and plenty of green spaces, making it a great location for professionals and families alike. Historically, the region has played a key role in British heritage, with significant contributions to industry, culture, and transportation.
HOW WILL IMG CONNECT SUPPORT YOU?
When applying with IMG Connect, you’ll have the full support of an expert recruitment team who will be your recruitment and relocation partners throughout the process. We\'ll support you with:
- CV preparation with a bespoke session with one of our specialists.
- Application support with expert knowledge of NHS specialisms & recruitment practice.
- At least two video calling interview preparation sessions.
- Contract and offer negotiations for salary, relocation packages, tenure, and more.
Once you have accepted your new role, you’ll then be supported and led throughout by one of our dedicated relocation executives who will guide you through all the way to starting your new role, including:
- Document gathering and checking.
- COS and Visa application support if applicable.
- Support sourcing short- and long-term accommodation.
- Travel arrangements and family support for finding schools and any other aspects of pastoral care.
Anyone requiring portfolio support (formally known as CESR) can have their required support discussed on a case-by-case basis.
JOB REQUIREMENTS AND DETAILS
- Candidates must hold MRCPsych (or equivalent) and be eligible for GMC registration with Specialist Registration in General Adult Psychiatry or within six months of gaining CCT.
- Prior experience in community or inpatient psychiatry is required.
- The salary will be between £105,504 - £139,882 per annum, dependent on experience.
- Provide clinical leadership for the Intensive Service team, ensuring high-quality home-based crisis care.
- Assess and treat patients referred to the Intensive Team, contributing to care planning and management discussions.
- Collaborate with inpatient services, community teams, and crisis services to support effective patient care.
- Participate in the teaching and development of junior doctors and multidisciplinary colleagues.
This region offers a balance of rural and urban living, with access to beautiful countryside, historic landmarks, and well-connected towns. Professionals moving to the area benefit from excellent schools, transport links, and a range of cultural and outdoor activities.
The region has a rich historical significance, featuring historic towns, world-renowned heritage sites, and a vibrant local community. It is a desirable location for families and professionals looking for a high quality of life.
HOW WILL IMG CONNECT SUPPORT YOU?
When applying with IMG Connect, you’ll have the full support of an expert recruitment team who will be your recruitment and relocation partners throughout the process. We\'ll support you with:
- CV Preparation with a bespoke session with one of our specialists.
- Application support with expert knowledge of NHS specialisms & recruitment practice.
- At least two video calling interview preparation sessions.
- Contract and offer negotiations for salary, relocation packages, tenure, and more.
- Document gathering and checking.
- COS and Visa Application support if applicable.
- Support sourcing short- and long-term accommodation.
- Travel arrangements.
- Family support for finding schools and any other aspects of pastoral care.